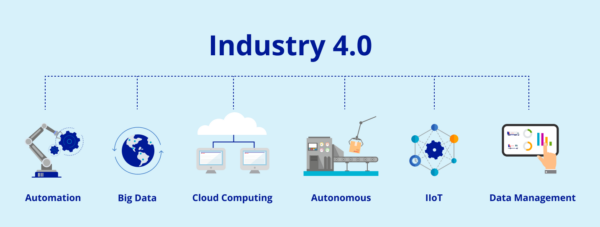
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0, is characterized by automation and technological advancements. It includes artificial intelligence (AI), big data, machine learning, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), robotics and more. More importantly, these technologies are now more closely connected to information and communication systems. These connections make it easier for manufacturers to scale, remain competitive and increase sustainability.
Industry 4.0 also sets the foundation for building smart factories where smart technologies are integrated in manufacturing processes. For example, machines can be enhanced with wireless connectivity, sensors and more while connected to a system that can visualize the entire production line and make independent decisions. Industry 4.0(fourth industrial revolution) technologies are also a strong foundation for future growth and innovation within the manufacturing sector.
In this article, we’ll explore the following questions and concepts:
- What is sustainable manufacturing, and why is it important?
- Smart supply chains for sustainable manufacturing
- Industry 4.0 applications in logistics and across the supply chain
- Challenges in adopting Industry 4.0 for sustainability
- The logistics perspective on Industry 4.0 and sustainability in manufacturing
- Manufacturing and sustainability for the future
It’s essential for manufacturers and businesses to understand Industry 4.0 because resilience and sustainability are critical for remaining competitive in a global market. A study conducted by the MPI Group showed that Industry 4.0 has already increased productivity and profitability. Here are some statistics to keep in mind:
- 63% of manufacturers using Industry 4.0 technology reported a profitability increase of over 5% compared to their previous year.
- 61% of companies recognize Industry 4.0 as a competitive differentiator.
- Another 37% say it will soon become a competitive differentiator.
Artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, autonomous vehicles, 3D printing, nanotechnology and quantum computing are some of the most talked about technologies and concepts driving Industry 4.0. They increase efficiency and productivity and will transform the shipping and manufacturing sectors in powerful new ways.
Many can also communicate across long distances and solve problems independently. Some of these exciting technologies are in their early stages, while others are quickly becoming more prevalent. Industry 4.0 is characterized by a range of leading-edge concepts and technologies including:

Smart supply chains for sustainable manufacturing
In today’s global market, the need for a sustainable and resilient supply chain is clear. Supply chains must be able to withstand unexpected geopolitical changes, shipping delays, material shortages and more. This is where a smart supply chain becomes critical.
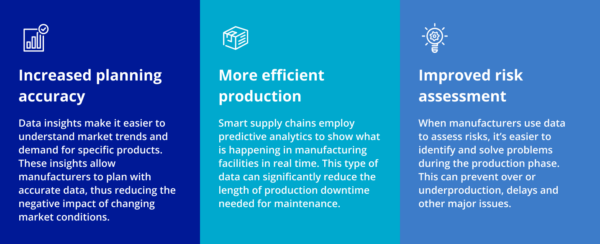
What is a smart supply chain? This type of supply chain uses automation, advanced technology and data to optimize operations. Smart supply chains are innovative, connected and help manufacturers operate efficiently and sustainably. They have a high degree of visibility and can therefore even promote small batch manufacturing, cutting costs and boosting sustainability. Here’s how smart supply chains help companies:
What is sustainable manufacturing, and why is it important?
The race to zero emissions is well underway across many industries. More than 5,200 businesses, including Purolator, have already pledged to meet net-zero targets by 2050.
Practical Decarbonization Strategies for Small and Mid-sized Businesses in 2024 and Beyond! Learn more
Our road to net-zero involves concrete goals like a 42% reduction in our absolute Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions by 2030. We are also working to:
- Reduce waste and increase recycling across our operations
- Decrease emissions by using alternative-fuel vehicles and optimized routes
- Expand sustainability in the supply chain by working with suppliers and customers to lessen Scope 3 emissions.
Thousands of other companies are also working towards net-zero, showing increased carbon emissions awareness. It also makes sustainable manufacturing more necessary and appealing than ever before.
What exactly is sustainable manufacturing? It’s a way of creating products that helps:
- Minimize adverse effects on the environment.
- Save energy and natural resources.
- Improve product and employee safety.
- Emphasize social responsibility.
- Promote the use of recyclable materials.
- Encourage partnerships with sustainable suppliers.
Manufacturing creates 30% of global greenhouse gas emissions according to a study from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). So it’s no surprise that reducing emissions and waste are the top priorities for the majority of manufacturers.
Sustainable manufacturing is important for a number of reasons. First, it benefits companies financially. It’s also important in terms of image because customers’ expectations around sustainability are changing.
At Purolator, we surveyed hundreds of Canadian and U.S. employees to better understand these changes. We discovered that:
- 50% of customers expect companies to use electric delivery.
- 67% think companies should be conserving or using renewable energy for their operations.
- 72.5% want to see companies reduce packaging.
How are companies responding? An overwhelming 87% of senior leaders said that sustainability is becoming more important, according to Fictiv’s Eighth Annual State of Manufacturing Report. However, 3 out of 10 companies said they struggled to develop the effective strategies needed to make their operations more sustainable. This is likely because many business owners feel they lack the necessary knowledge and skills to increase sustainability.
Industrialization contributes greatly to economies around the world. The challenge lies in continuing to fuel economic growth through industrialization while reducing the environmental impact of that growth.
Governments must step in to help businesses with sustainable development goals (SDGs), which need to be met by 2030 as set out by the United Nations.
Around 49% of businesses and 44% of citizens believe governments are the primary entity responsible for achieving SDGs. This is according to PwC research.
Below are 5 of the 17 SDGs. These ones in particular present the greatest opportunities for most manufacturers.

Industry 4.0 applications in logistics and across the supply chain
Now that we’ve discussed the importance of sustainability in the supply chain and in manufacturing, let’s explore what that looks like in action. Here are some Industry 4.0 examples where data, technology and even partnerships with established shipping and logistics providers increase overall efficiency and reduce costs.
A general overview of the manufacturing supply chain
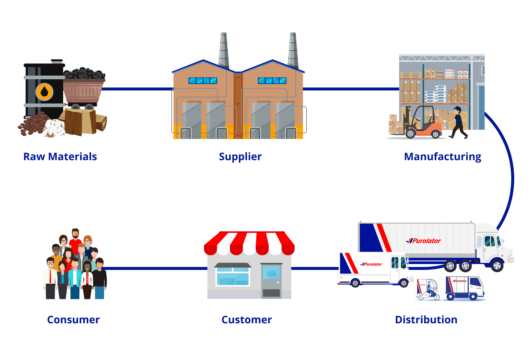
Bring your logistics and supply chain into the future with Industry 4.0
 Business planning, processes and logistics
Business planning, processes and logistics
Real-time tracking and data transparency
- Transparency is crucial to any company’s sustainability progress. Real-time data tracking coupled with increased transparency helps manufacturers keep a close eye on demand, trends and patterns. With this information, they can make more informed decisions on a local and global scale. For example, using Industry 4.0-style data and tracking can help manufacturers create a green supply chain where they better understand which products are in demand, thus reducing waste.
- Keeping track of market demand and changes can be challenging. Businesses can partner with an experienced logistics partner like Purolator which works to support manufacturers and help them respond to market fluctuations.
Optimize shipping to reduce emissions
- Companies can leverage data to identify shipping and packaging inefficiencies. This helps determine where shipments can be consolidated to save on costs.
- Partnering with an eco-conscious shipping and logistics provider also optimizes shipping. The ideal provider will offer consolidated shipping, sustainable packaging help, optimized routes and green delivery options using e-bikes, electric, hybrid and autonomous vehicles.
- Eco-friendly packaging improves the shipping process overall. This includes secure but reduced and “right-size” packaging, recycled filler material, recyclable padded mailers and more.
- Better shipping and sorting efficiency also reduces emissions. Purolator’s National Hub uses automation to triple the facility’s sorting capacity to a rate of up to 48,000 parcels per hour. Purolator also uses electric and hybrid vehicles for shipping. As of 2022, the hub produced a 15% gain on energy usage and emitted about 439,000 fewer kilograms of carbon.
Energy and emission management
- Applications of Industry 4.0, including robotics, renewable energy, data collection and forecasting, IIoT and digitalization technologies used for research and development. This covers solar energy consumption, energy safety and lightweight materials to lower a company’s carbon footprint.
- There are many ways that manufacturers can increase energy efficiency including investing in battery storage systems and renewable energy resources. Companies can also retrofit for efficiency by replacing fluorescent and incandescent light bulbs with LEDs.
Service management
- Industry 4.0 links measurement instruments to the complete knowledge and automation infrastructure of a manufacturer. This is an extension of collecting, transferring and storing capabilities of vast data volumes related to energy supply use, production and transition.
- The growth of data and increased access to computer resources enables special AI techniques to facilitate variable detection and analyze trends and patterns in various industries.
Digitizing and modernizing tracking capabilities
- By digitizing and modernizing tracking capabilities, businesses can easily eliminate inefficiencies by providing total visibility of a manufacturing plant. Digitization typically involves embedded sensors in manufacturing equipment that connect to cyber-physical systems. The benefits include reduced errors, lower production costs and higher capabilities to meet market demands.
 Warehouse environments
Warehouse environments
Sustainable smart factories
- Industry 4.0 technologies drive responsible consumption and development for businesses through connected factory equipment, AI-enabled energy systems and IIoT devices.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and warehousing
- RFID technology identifies people and objects using radio waves. In a warehouse setting, manufacturers use RFID technology and tags to track products and even locate lost items. RFID can also minimize waste in production and logistics processes because it can replace paper receipts and labels, reduce shipping errors and trace products to cut down on wasted materials.
Sustainable buildings
- Digital technologies and building information modeling software can optimize buildings by incorporating elements such as eco-friendly bacteria that naturally repair structures into industrial and commercial structures.
- Energy-efficient heating and cooling systems will self-regulate in real time, saving energy and lowering the cost of electricity for manufacturers. Sensors and IIoT Industry 4.0 devices can tell environmental control systems to switch off the lights and air conditioning when people leave a building.
- Purolator’s National Hub was designed to meet the requirements of the Toronto Green Standards program and optimize shipping efficiency. The building itself reduces energy use and waste with high-albedo concrete for less energy consumption. It also uses a wastewater reclamation system and a grey water reclamation system that can hold one million liters.
Performing jobs
- Machine learning is a branch of AI where computers can be programmed to take data and make decisions, eliminating the need to code the machine to perform a job. There are opportunities to include small and medium-sized businesses in AI advancement through education, strategic investment, grants, task forces and advanced research initiatives. This education also helps ensure that personal and company data are not misused.
 Waste management
Waste management
Waste control and resource optimization
- The concentration of low-cost sensors with integration and big data analysis appears to contribute to effective manufacturing systems. These innovations provide suppliers with new insights into how to optimize their manufacturing processes, sustainability and supply chain management for reduced prices and improved customer experience. Smart production practices also minimize waste and greenhouse gas pollution, whether by mistake or design.
- A number of IIoT technologies can help manufacturers use less energy and reduce production waste by allowing them to monitor multiple factors simultaneously including energy output, performance, maintenance needs and more.
Challenges in adopting Industry 4.0 for sustainability
A smart factory using Industry 4.0 technology is the ultimate goal for many manufacturers. After all, eco-conscious manufacturing has countless environmental and financial benefits including efficiency, waste reduction and less energy and natural resource consumption.
However, the road to sustainable Industry 4.0 manufacturing has its obstacles such as lack of control over suppliers’ and partners’ commitment practices and trouble scaling. Many companies struggle to update their processes and operations. Below are some of the biggest challenges companies face as they adopt an Industry 4.0 strategy and work toward sustainability:
Smart equipment requirements
Smart equipment should be able to collect production information, provide compatible data interface and support generic communication protocol. Flexible manufacturing is a typical feature of a smart factory, but there are still many challenges in terms of production line such as dynamic scheduling and tight coupling between functions and devices.
The need for networks to be deeply integrated
The IIoT facilitates a deep integration of information and industrialization. Advanced IIoT technology is important for the implementation of the smart factory. However, standards have not yet been formed in the field of Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks (IWSNs). The standardization process must be promoted continuously. In the complicated electromagnetic environment, data transmission should meet the requirements of reliability and real-time equipment control.
Changing customer expectations
As Industry 4.0 trends emerge, customers expect manufacturers to adopt new technology accordingly. They want a seamless experience, more flexibility and less manual or administrative work. This translates to faster shipping times, more productive manufacturing plants and highly personalized customer service. Essentially, businesses need to leverage Industry 4.0 technology to transform how they interact with customers. Improving the customer experience can include using AI chatbots learning about customers’ behaviour and habits. It can also mean incorporating more robotics and data analysis on the factory floor to efficiently meet changing market demands and trends.
Network security
Because of the access granted to large-scale devices, network security also becomes very important. Advancements in information technologies have produced significant progress in industrial wireless networks. These technologies include the Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT), LTE-Advanced, 5G,and Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Progress has provided new solutions for key IWSN issues, such as reliability, real-time performance, energy efficiency and security strategy.
A concrete plan to reduce scope emissions
According to a survey conducted by Fictiv and Dimensional Research, nearly 33% of manufacturers say a lack of knowledge about how to create a “concrete sustainability plan” is one of their biggest challenges. This is an especially significant issue for small and medium enterprises that want to create practical decarbonization strategies. These businesses can get started by:
- Choosing more eco-friendly packaging.
- Partnering with sustainable suppliers.
- Understanding their own emissions.
- Exploring zero-emission and low-carbon shipping options.
To develop an actionable plan, some manufacturers may also need consultants to help tackle complex supply chains and gather sufficient data. Autonomous, hybrid and electric vehicles—along with consolidated shipping—can also be a significant help on the path to net-zero.
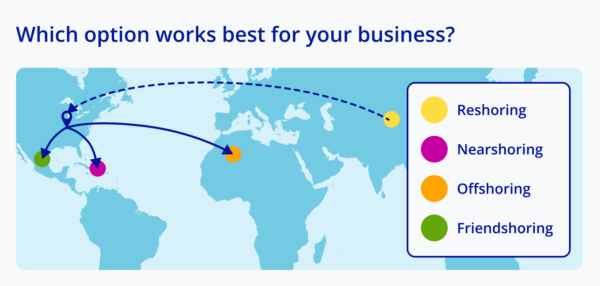
It all begins with manufacturers focusing on what they can change in terms of sustainability and supply chain management. Some manufacturers will need to shift their procurement approach to lessen their environmental impact. This is where nearshoring, reshoring, offshoring and friendshoring come into play.
For example, nearshoring between the U.S. and Mexico means getting raw materials from a nearby, reliable and stable supplier. As a result, businesses produce less carbon emissions from transportation. They’re also less likely to be surprised by destabilizing events and supply chain disruptions.
When choosing the best strategy be sure to consider:
- Shifts in the market.
- Spend analysis.
- Supplier options.
- Changes to consumer behaviour.
Is it time to rethink your sourcing strategy? Improve costs and reduce emissions with more advantageous procurement partnerships. Learn more
The logistics perspective on Industry 4.0 and sustainability in manufacturing
Developments in the realm of Industry 4.0 and sustainability give the logistics industry a lot to consider. There’s still much to address in terms of how to make supply chains more sustainable and optimize shipping processes.
There are also some important emerging Industry 4.0 supply chain trends to keep an eye on.
Below is a breakdown of the primary steps that take each shipment from initial order through delivery and reverse logistics (if needed).
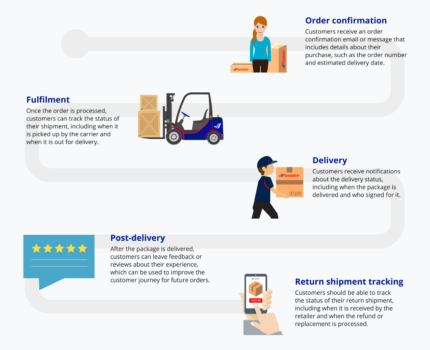
There are many ways to boost sustainability and leverage Industry 4.0 technologies throughout this journey. These examples include important factors and capabilities to consider when looking for a logistics provider.
- IIoT and AI
-
- The IIoT and AI can improve production and the supply chain to save companies money. Companies can use data for predictive analytics and demand forecasting. This means they can predict trends and produce an inventory that’s aligned with real-time market changes. AI and the IIoT can also work with sensors to provide information on energy usage and weak points so facilities can become more energy efficient.
-
- Real-time data
-
-
- Companies can use real-time data to better understand cost-effective and eco-friendly packaging options. This includes right-size packaging and using fewer packing materials that are recyclable or compostable. When done well, eco-friendly packaging is still secure and can even make returns or reverse logistics easier for customers.
- Paired with tracking, real-time data can provide full visibility of a manufacturing plant. Companies can ensure sustainable and efficient manufacturing practices at every stage of production and look into ethical sourcing if needed.
- Real-time data also offers real-time tracking, which can increase shipping security. This modernized form of tracking can also improve ongoing route optimization and identify the most efficient last-mile delivery approach.
-
- Robotics
-
-
- On the factory floor, workers typically perform many repetitive tasks. Robotics will reduce costs while increasing productivity and worker safety. By boosting efficiency and sometimes even supporting small batch production, Industry 4.0 technologies like robotics have the potential to make virtually all manufacturers more sustainable.
- The potential of robotics in logistics cannot be overstated. Purolator’s National Hub also uses robotics to triple parcel sorting capacity and get shipments out faster and more efficiently than traditional facilities.
-
- Autonomous vehicles
-
-
- Real-time data has the potential to optimize shipping routes. On those shipping routes, companies should work with a logistics provider that uses autonomous vehicles. This practice keeps carbon emissions down and can get shipments to their destination more efficiently.
-
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
-
- Manufacturers can use AI in logistics and supply chain management. Leveraging AI and machine learning allows for proactive problem solving, risk management and route optimization. In terms of customer service, chatbots can monitor habits and collect data during each customer interaction, allowing businesses to better anticipate customers’ needs.
The future of sustainable logistics is bright for manufacturing companies. The key is learning more about the concepts and technologies that are available and understanding how they can be used on the factory floor and between shipping destinations.
Manufacturing and sustainability for the future
Businesses must also take concrete steps to ensure they are continually adapting if they are to effectively address the challenge at hand.
There will be obstacles along the way as these technologies continue to advance, but leveraging Industry 4.0 technology can make the journey easier and result in a better long-term business outlook. Companies can increase their overall efficiency, transparency with partners and customer and sustainability throughout the supply chain by using Industry 4.0 technologies in their logistics operations.
Remember, this technology isn’t just for industry giants. Small and medium-sized business owners can benefit greatly from adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. The key is to provide adequate employee training to ensure a smooth transition to an increasingly digitized factory floor. Small and medium-sized businesses that emphasize the customer experience have a significant competitive advantage. Therefore, they can also benefit from Industry 4.0 technologies like AI and machine learning that help provide personalized customer service.
Savvy customers expect personalized service and want manufacturers to be aware of their environmental impact. Therefore, manufacturers must consider how to create green supply chains. Along the way, it’s also critical to promote transparency with partners and suppliers to ensure a smart, connected and sustainable supply chain.
Across industries, data is at the core of becoming part of and benefitting from Industry 4.0 advancements. Working with data creates a strong foundation for a smarter supply chain and sustainable operations. Therefore, collecting and analyzing data should be top of mind for manufacturers.
Companies that stay ahead of the curve by adopting these Industry 4.0 technologies and approaches will benefit from reduced costs and environmental impact while still meeting the demands of sustainability-focused customers.